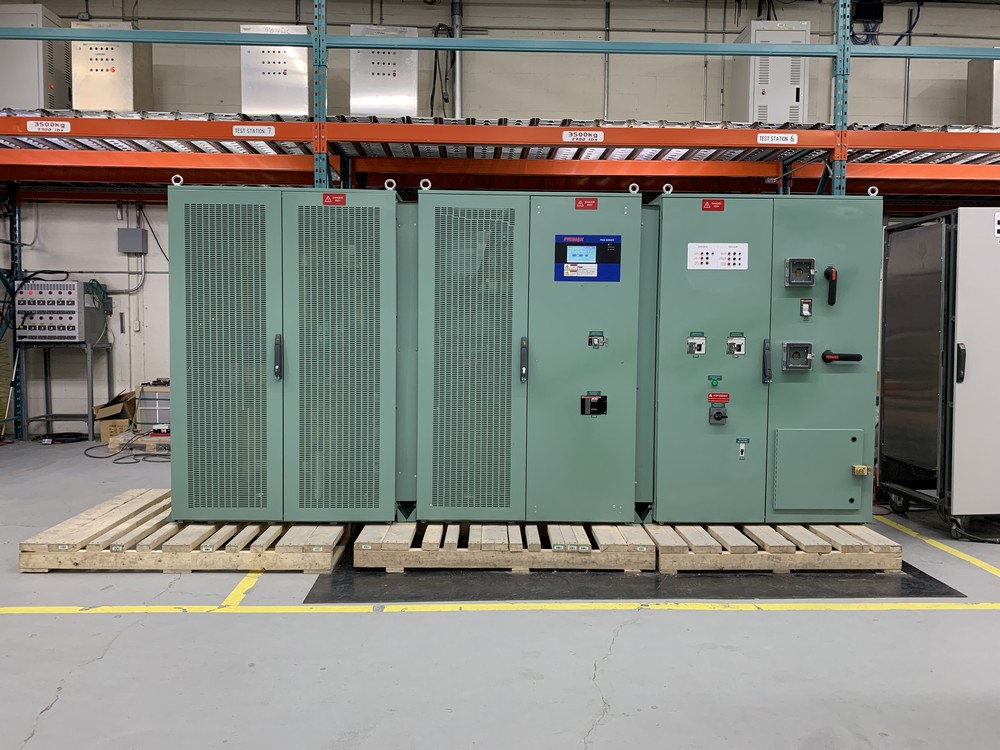
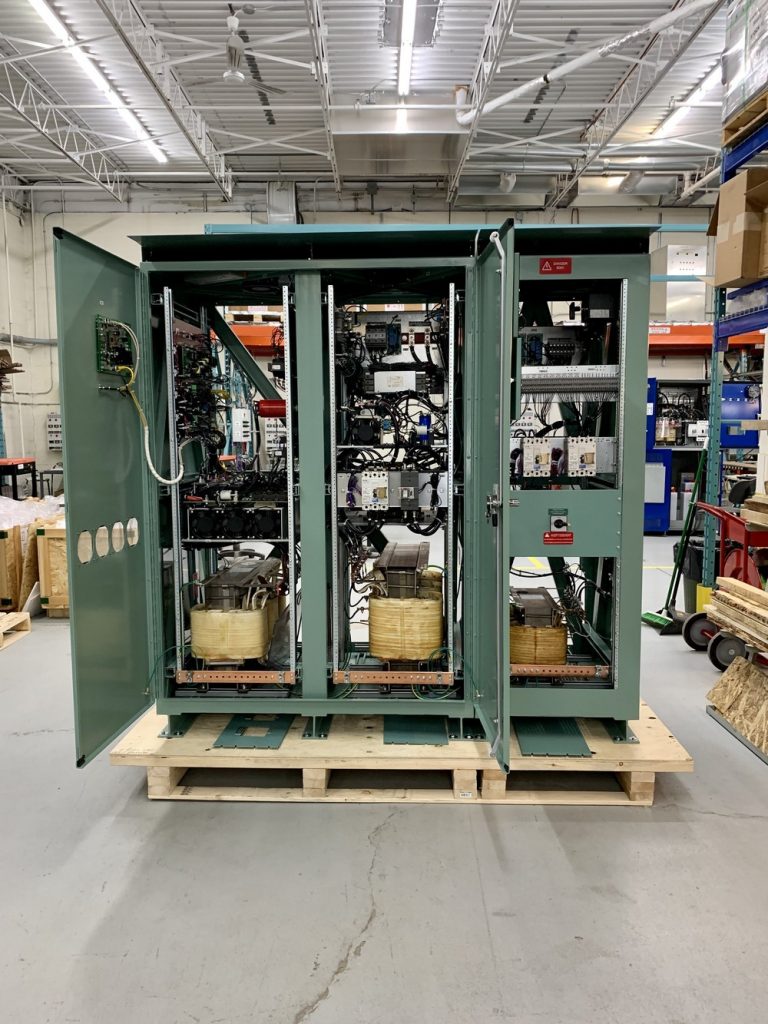
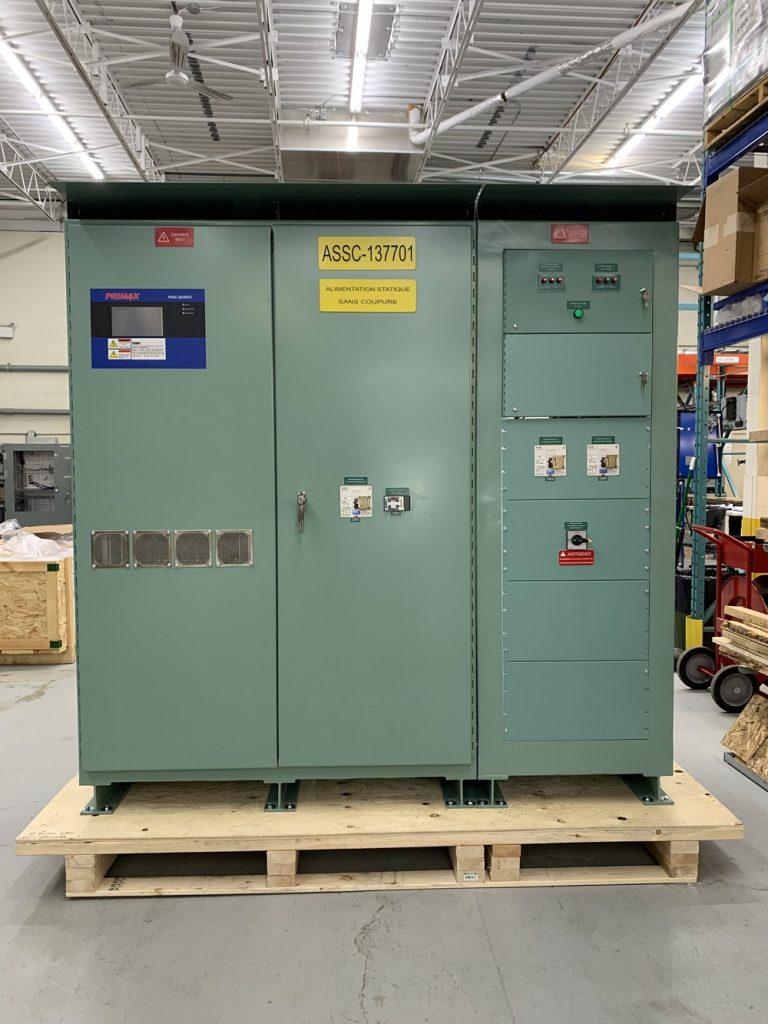
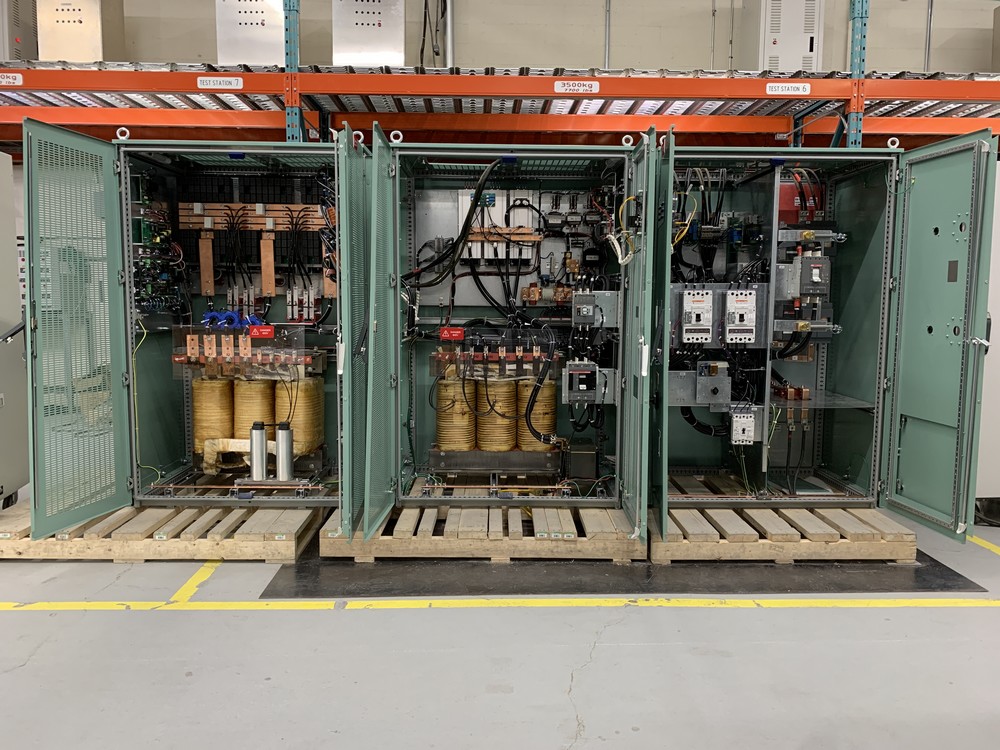
Why industrial grade UPS?
Industrial grade P850u UPS, in contrast with IT (server) grade UPS, are generally installed in uncontrolled environment and fed from relatively poor quality electrical sources. They usually feed an unbalanced mix of industrial equipment and IT systems in a polluted and uncontrolled temperatures: ex. motors, lights, sensitive process equipment, telecom equipment, small servers, etc.
As a matter of fact in industrial plants, electrical sources usually have sever power quality issues due to the complexity of the other connected loads: Harmonics, unbalanced loading, voltage dips and sags, flickers, spikes and surges, over and under voltage, voltage variations, interruptions, frequency fluctuations, outages and short interruptions are few factors to be considered.
So what should we consider for an industrial grade UPS?
- Input protection: Circuit breakers, surges, EMI and transient protection
- Input transformer with double shielding
- IEEE 2405 / NEMA PE5 compliant charger/rectifier
- Longer battery backup time ex. 2 hours to deploy necessary efforts to secure the process and restore the power.
- Battery recharge time within 8-10 hours.
- Static switch (STS): full SCR (not hybrid with contactors) on the inverter and the bypass side, sized for worst load fault case.
- Manual bypass switch (MBS): shall be rotary make-before-break manual switch installed in a separate enclosure. Breaker and contactor switching is not accepted.
- Special wiring: Halogen free-SIS, Tefzel, etc.
- Minimum 20 year life design.
- Spares must be available for over 12 years.
What about harsh and corrosive environment protection?
Failures due to contaminants and corrosive agents such as mild acids (hydrochloric, sulfuric), high humidity, salt and alkaline agents can be very costly. Failure of a simple component such as a switch or a busbar, can lead to a loss of reliability of the backup system. Corrosion and contaminants cannot be eliminated but they should be properly addressed and managed at the time of the design of the system. As an example in an acidic environment:
- UPS should be fully sealed within continuously welded enclosure c/w air conditioning to prevent contaminants from entering any nooks or gaps.
- Use appropriate grade stainless steel where ever possible.
- Use of non-metallic framing and struts.
- Use coated copper busbars to minimize contact of fine dust or fume.
- Use stainless steel terminal blocks whenever is possible.
- Use No-Ox grease on all electrical connections.
- Tripple coat all PCBs with silicone. Ideally, epoxy coating all pcbs.
- Regular maintenance and dusting off.
Other important considerations?
- 3ph input with 1ph output: Single phase output design can help into clearing downstream faults better than 3 phase design. Plus the fact that with single phase you should not be concerned about phase balancing.
- External maintenance bypass switch (MBS): We do not recommend having the MBS integral within the UPS. For safety issues, the MBS shall be external.
- Regulating bypass transformer: We recommend using electronic type regulating transformer to help protecting the critical load when it’s fed by the unregulated bypass line.
- Emergency Power Off switch (EPO): terminal blocks shall be provided to be connected to a remote EPO for safety, ideally next to entrance door far away from the UPS. The EPO function shall shunt trip all energy sources breakres: AC in, battery, bypass in.
- Communication: Modbus communication is preferred. Events log shall also be include locally (on the LCD) and remotely.
- Alarm relays: rated 120Vac/240Vac-10A, (L/R to be specified if needed)
- Alarm terminal blocks: shall be of the DIN rail type for #14GA wire.
- 4-20mA signals: shall be provided for output voltage and current.
Factors to size an industrial UPS?
First, you need to define the mix of linear and non linear loads with their specifics: hold up time, constant or intermittent, operation time, inrush and nonlinear, etc with a special attention to the following:
- Non linear loads: VFD (motor drives) with no harmonic compensation, Scada systems…
Require crest factor of 3:1 based on the rms current reading not on the peak current to prevent unexpected load transfers. - Cold start inrush currents: depending on the inrush vs. The size of the UPS, equipment creating start inrush currents would be started via the static switch and the bypass line. Such loads static switch will have a minimum of 1000% rating for one cycle based on the inverter’s full load capacity.
- Load harmonics: non-linear loads 3rd, 5th, 7th harmonic contents are very considerable. UPS output transformers and bypass transformers shall be capable to support such load. Preferably K-20 rated transformers shall be used in case of feeding VFDs or computer loads. Class 105 transformers (50C temperature rise) is recommended for long term reliability.
- Black start capability: Loads can be required to be powered before the utility being connected to site. i.e. UPS will be started with battery only or with temporary generator which can be a not very well stabilized source.
What about your battery?
Batteries in industrial application should be compatible with the plant operation conditions. Battery grade, technology, redundancy, available maintenance crew knowledge, outage time are few factors to be considered. for example, in plant with frequent power interruptions, battery with high cycling capabilities may be needed. similarly, if human life is in play, batteries with the less probability to fail open should be selected. In the following, few specifics are listed:
- 20 year design life.
- Size batteries with applicable IEEE standards including aging, design and temperature factors.
- AGM VRLA batteries are not recommended.
- Ni-Cd type is preferred over lead-acid for the following reasons:
– Ni-Cd battery does not experience open cell/circuit failure.
– Ni-Cd battery electrolyte specific gravity is stable throughout the discharge cycle. In cold environment event, the Ni-Cd freezing temperature is very low when battery is fully discharged. - Li-Ion can be a very good option for redundancy, space, weight, maintenance and battery state of health continuous reporting.
- Whenever possible, use a common battery to feed different systems. Ex. when ac loads need backup, use the station battery (ex. 125Vdc) to feed an inverter instead of installing a complete UPS system.
- Lower number of cells to help service and prevent cell unbalancing over the life of the system. Ex. 125Vdc battery for systems up to 60kVA, 250Vdc for systems up to 250kVA.
- Battery end voltage: 1.75Vpc for lead acid and 1.14Vpc for Ni-Cd. Lower voltages are not acceptable.
- Low current and voltage ripple to prevent both inverter and charger imposed ac ripple (current and voltage) from affecting the battery life.
- Battery continuity testing capabilities embedded in the UPS.
Small AC and DC distribution panels, integrated battery and dual redundant chargers are few of many attractive options that can be included in our product.